Busi, Susheel et al. Microbiology Spectrum (2023)
Abstract
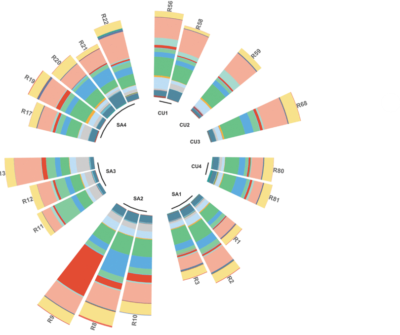
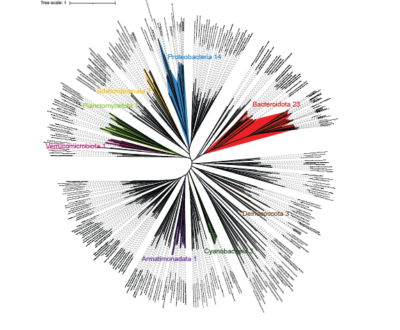
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a universal phenomenon the origins of which lay in natural ecological interactions such as competition within niches, within and between micro- to higher-order organisms. To study these phenomena, it is crucial to examine the origins of AMR in pristine environments, i.e., limited anthropogenic influences. In this context, epilithic biofilms residing in glacier-fed streams (GFSs) are an excellent model system to study diverse, intra- and inter-domain, ecological crosstalk. We assessed the resistomes of epilithic biofilms from GFSs across the Southern Alps (New Zealand) and the Caucasus (Russia) and observed that both bacteria and eukaryotes encoded twenty-nine distinct AMR categories. Of these, beta-lactam, aminoglycoside, and multidrug resistance were both abundant and taxonomically distributed in most of the bacterial and eukaryotic phyla. AMR-encoding phyla included Bacteroidota and Proteobacteria among the bacteria, alongside Ochrophyta (algae) among the eukaryotes…
Ezzat, Leïla et al. Applied and Environmental Microbiology (2022)
Abstract
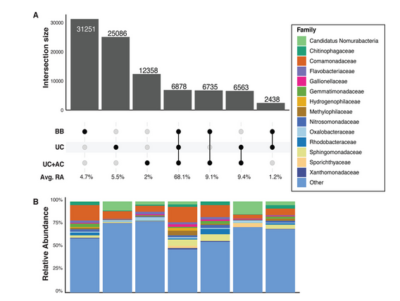
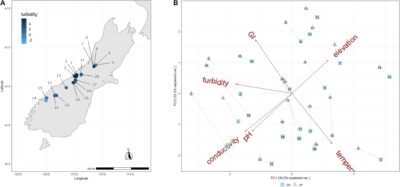
Microbial life in glacier-fed streams (GFSs) is dominated by benthic biofilms which fulfill critical ecosystem processes. However, it remains unclear how the bacterial communities of these biofilms assemble in stream ecosystems characterized by rapid turnover of benthic habitats and high suspended sediment loads. Using16S rRNA gene amplicon sequence data collected from 54 GFSs across the Himalayas, European Alps, and Scandinavian Mountains, we found that benthic biofilms harbor bacterial communities that are distinct from the bacterial assemblages suspended in the streamwater. Our data showed a decrease in species richness in the benthic biofilms compared to the bacterial cells putatively free-living in the water. The benthic biofilms also differed from the suspended water fractions in terms of community composition…
Bourquin, Massimo et al. Nature Communications (2022)
Abstract
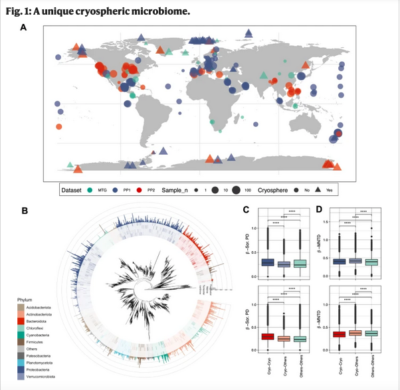
The melting of the cryosphere is among the most conspicuous consequences of climate change, with impacts on microbial life and related biogeochemistry. However, we are missing a systematic understanding of microbiome structure and function across cryospheric ecosystems. Here, we present a global inventory of the microbiome from snow, ice, permafrost soils, and both coastal and freshwater ecosystems under glacier influence. Combining phylogenetic and taxonomic approaches, we find that these cryospheric ecosystems, despite their particularities, share a microbiome with representatives across the bacterial tree of life and apparent signatures of early and constrained radiation…
Bhanu Busi, Susheel, et al. Nature Communications (2022)
Abstract
In glacier-fed streams, ecological windows of opportunity allow complex microbial biofilms to develop and transiently form the basis of the food web, thereby controlling key ecosystem processes. Using metagenome-assembled genomes, we unravel strategies that allow biofilms to seize this opportunity in an ecosystem otherwise characterized by harsh environmental conditions. We observe a diverse microbiome spanning the entire tree of life including a rich virome. Various co-existing energy acquisition pathways point to diverse niches and the exploitation of available resources, likely fostering the establishment of complex biofilms during windows of opportunity. The wide occurrence of rhodopsins, besides chlorophyll, highlights…
Kohler, Tyler J., et al. Global Change Biology (2022)
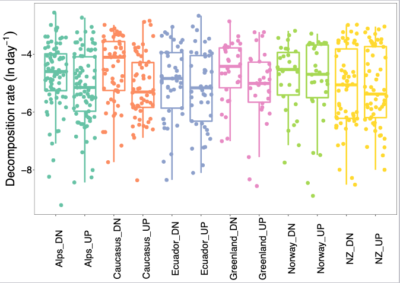
Abstract
The shrinking of glaciers is among the most iconic consequences of climate change. Despite this, the downstream consequences for ecosystem processes and related microbiome structure and function remain poorly understood. Here, using a space-for-time substitution approach across 101 glacier-fed streams (GFSs) from six major regions worldwide, we investigated how glacier shrinkage is likely to impact the organic matter decomposition rates of benthic biofilms. To do this, we measured the activities of five common extracellular enzymes and estimated decomposition rates by using enzyme allocation equations based on stoichiometry. We found decomposition rates to…
Fodelianakis Stilianos, et al. ISME (2021)
Abstract
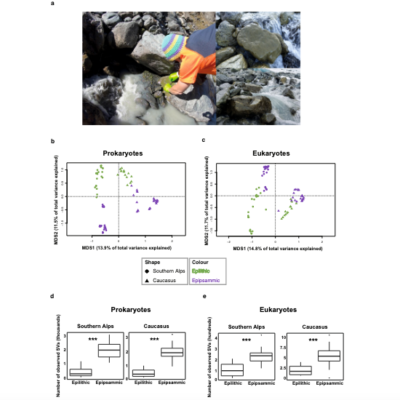
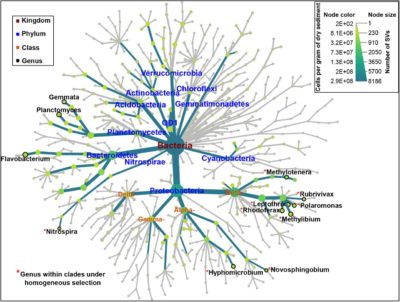
Glacier-fed streams (GFSs) are extreme and rapidly vanishing ecosystems, and yet they harbor diverse microbial communities. Although our understanding of the GFS microbiome has recently increased, we do not know which microbial clades are ecologically successful in these ecosystems, nor do we understand potentially underlying mechanisms. Ecologically successful clades should be more prevalent across GFSs compared to other clades, which should be reflected as clade-wise distinctly low phylogenetic turnover. However, methods to assess such patterns are currently missing. Here we developed and applied a novel analytical framework, “phyloscore analysis”, to identify clades with lower spatial phylogenetic turnover than other clades in the sediment microbiome across twenty GFSs in New Zealand. These clades constituted up to 44% and 64% of community α-diversity and abundance, respectively. Furthermore…
Busi SB, et al. BIOXRIV (2021)
Abstract
Microorganisms dominate life in cryospheric ecosystems. In glacier-fed streams (GFSs), ecological windows of opportunities allow complex microbial biofilms to develop and transiently form the basis of the food web, thereby controlling key ecosystem processes. Here, using high-resolution metagenomics, we unravel strategies that allow biofilms to seize this opportunity in an ecosystem otherwise characterized by harsh environmental conditions. We found a diverse microbiome spanning the entire tree of life and including a rich virome. Various and co-existing energy acquisition pathways point to diverse niches and the simultaneous exploitation of available resources, likely fostering the establishment of complex biofilms in GFSs during windows of opportunity. The wide occurrence of rhodopsins across metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs), besides chlorophyll, highlights the role of solar energy capture in these biofilms. Concomitantly…
Kohler, Tyler J., et al. Frontiers in Microbiology (2020)
Abstract
Glacier-fed streams (GFSs) exhibit near-freezing temperatures, variable flows, and often high turbidities. Currently, the rapid shrinkage of mountain glaciers is altering the delivery of meltwater, solutes, and particulate matter to GFSs, with unknown consequences for their ecology. Benthic biofilms dominate microbial life in GFSs, and play a major role in their biogeochemical cycling. Mineralization is likely an important process for microbes to meet elemental budgets in these systems due to commonly oligotrophic conditions, and extracellular enzymes retained within the biofilm enable the degradation of organic matter and acquisition of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P). The measurement and…
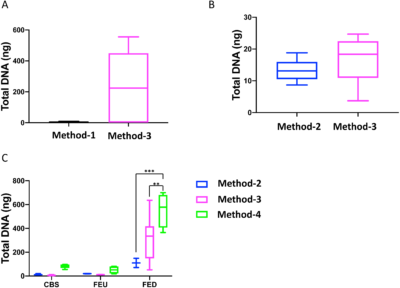
Busi SB, et al. PeerJ (2020)
Abstract
Glacier-fed streams (GFS) are harsh ecosystems dominated by microbial life organized in benthic biofilms, yet the biodiversity and ecosystem functions provided by these communities remain under-appreciated. To better understand the microbial processes and communities contributing to GFS ecosystems, it is necessary to leverage high throughput sequencing. Low biomass and high inorganic particle load in GFS sediment samples may affect nucleic acid extraction efficiency using extraction methods tailored to other extreme environments such as deep-sea sediments. Here, we benchmarked the utility and efficacy of four extraction protocols, including an up-scaled phenol-chloroform protocol. We found that established protocols for comparable sample types consistently failed to yield sufficient…